
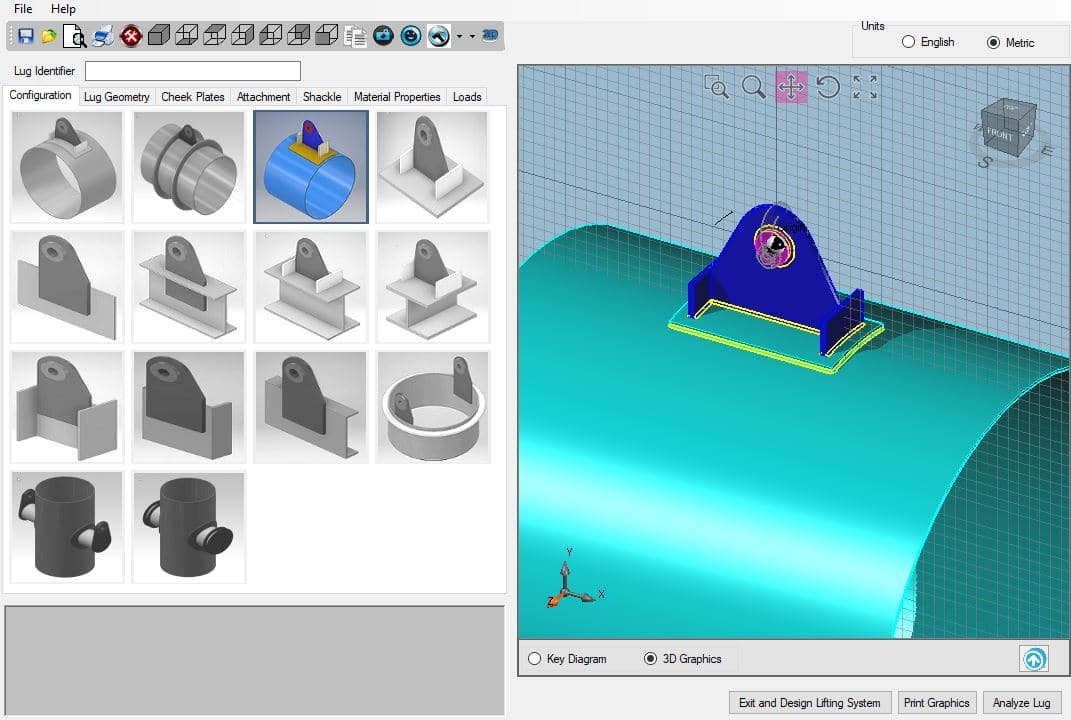
Shear failure occurs on the axis parallel to the force of lift. This load will designated the largest load the lug and shackle may carry safely at that specific angle of engagement. Tension failure occurs along the axis perpendicular to the force of lift and must be considered along all the possible angles of lift, for which a maximum load may assigned. Common modes of failure are tension, shear, bearing, and hoop tension. The load calculations take into consideration all the different ways a lifting lug may fail. As the typical industrial applications of a lifting lug pose immense safety risks in the incident of failure, heavy load analysis calculations must be considered when making one. Lifting lugs are designed with the load and range of load that it can carry in mind. Courtesy: Bishop Lifting Lifting Lug Design Courtesy: Winsafe In this article you will learn about how lifting lugs are designed, different types, and how they are fabricated, installed, and tested. They are also essential in the mobility of crates, containers, and other devices on large scale operations like oil rigs. In the world of engineering, industrial-scale lifting lugs move large containers and other heavy loads. Lifting lugs are designed mounting points that help carry an object or equipment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
